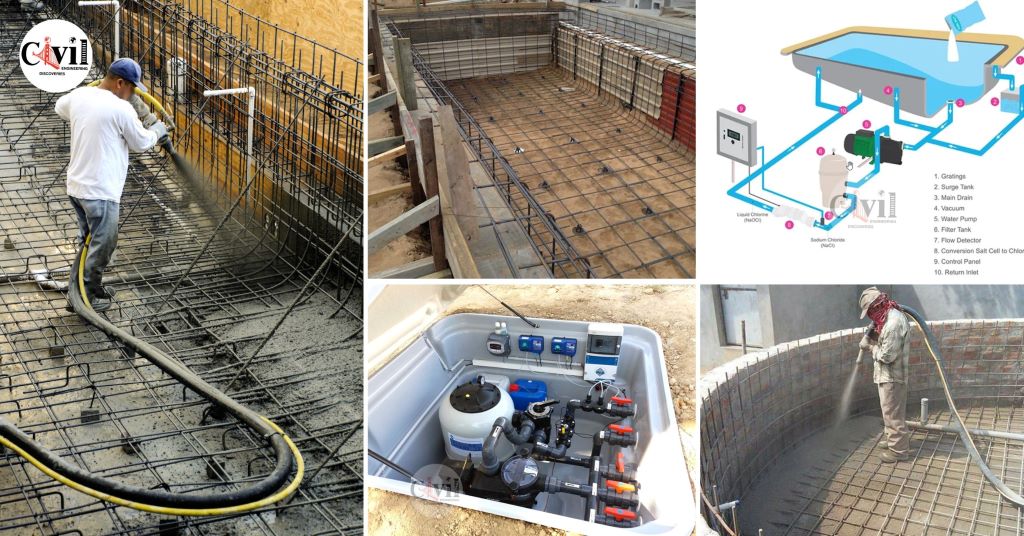
The shimmering allure of a concrete pool beckons, promising endless summer days and tranquil evenings. But beneath the inviting surface lies a complex interplay of engineering, material science, and meticulous craftsmanship. A concrete pool isn’t just a hole in the ground filled with water; it’s a carefully designed structure that must withstand immense hydrostatic pressure, soil movement, and the relentless forces of nature. Understanding the intricacies of concrete pool structural design is crucial for ensuring longevity, safety, and a seamless aquatic experience.
Laying the Foundation: Soil Analysis and Site Preparation
The journey begins long before the first shovel hits the earth. A comprehensive soil analysis is paramount, revealing the soil’s composition, bearing capacity, and potential for movement. Expansive clay soils, for instance, can swell and shrink with moisture changes, exerting significant stress on the pool structure. Geotechnical engineers analyze soil samples to determine the appropriate excavation depth, the need for soil stabilization, and the optimal foundation design. This analysis dictates the pool’s overall structural integrity, preventing costly and potentially catastrophic failures. Site preparation involves clearing vegetation, grading the land for proper drainage, and compacting the soil to ensure a stable base. This meticulous preparation lays the groundwork for a pool that can withstand the test of time.
The Blueprint of Strength: Structural Engineering Principles
Concrete pools are designed using fundamental structural engineering principles. The pool shell, typically constructed from reinforced concrete, acts as a self-supporting structure. The design must account for hydrostatic pressure, the force exerted by the water on the pool walls and floor. This pressure increases with depth, demanding robust reinforcement to prevent cracking and deformation. Engineers calculate the required concrete thickness, reinforcement bar size, and spacing based on the pool’s dimensions, depth, and anticipated water load. Finite element analysis (FEA) software is often employed to simulate the pool’s behavior under various loading conditions, ensuring structural integrity and optimizing material usage.
The Backbone: Reinforcement and Concrete Mix Design
Reinforcement, typically in the form of steel rebar, is the backbone of the concrete pool. It provides tensile strength, counteracting the forces that would otherwise cause the concrete to crack. The rebar is arranged in a grid-like pattern, forming a cage that encases the pool shell. The spacing and size of the rebar are critical, ensuring adequate reinforcement throughout the structure. The concrete mix design is equally vital. A high-quality concrete mix, with the right proportions of cement, aggregates, and water, is essential for achieving the required strength and durability. Admixtures, such as plasticizers and water reducers, are often added to enhance workability and improve concrete performance. Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete, is commonly used for pool construction due to its ability to conform to complex shapes and create a monolithic structure.
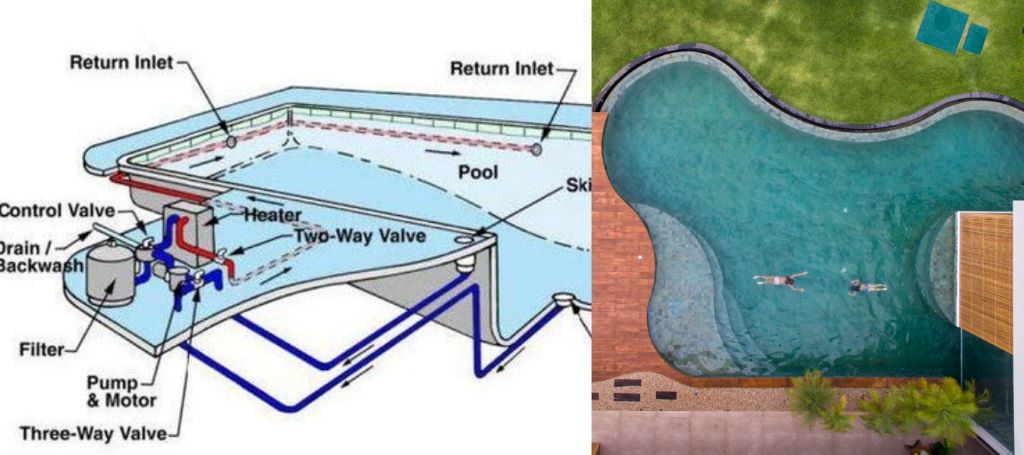
Waterproofing and Expansion Joints: Preventing Leaks and Cracks
Concrete, while strong, is inherently porous. Waterproofing is crucial to prevent water seepage and protect the reinforcement from corrosion. Various waterproofing methods are employed, including applying cementitious coatings, epoxy sealants, or elastomeric membranes. Expansion joints are also incorporated into the pool design to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction, as well as minor ground movements. These joints, typically made of flexible materials, prevent cracking by allowing the concrete to move independently. Skimmer lines, return jets, and other penetrations through the pool shell are meticulously sealed to prevent leaks.
The Art of Shaping: Freeform and Geometric Designs
Concrete pools offer unparalleled design flexibility, allowing for the creation of freeform and geometric shapes. Freeform pools, with their organic curves and flowing lines, blend seamlessly into natural landscapes. Geometric pools, with their clean lines and sharp angles, exude a modern and sophisticated aesthetic. The design process involves creating detailed plans and 3D models, ensuring accurate dimensions and seamless integration with the surrounding environment. The shaping of the pool shell is a skilled craft, requiring precise formwork and meticulous concrete placement. Experienced pool builders can transform intricate designs into stunning aquatic masterpieces.
Beyond the Shell: Plumbing, Filtration, and Finishes
The structural design extends beyond the pool shell to encompass the plumbing and filtration systems. Proper plumbing design ensures efficient water circulation and filtration, maintaining water quality and clarity. Skimmers, main drains, and return jets are strategically placed to optimize water flow. The filtration system, including pumps, filters, and sanitizers, removes debris and contaminants, keeping the water clean and safe. The interior finish, such as plaster, tile, or pebble, adds the final touch of elegance and functionality. These finishes provide a smooth and durable surface, enhancing the pool’s aesthetics and longevity.
Ensuring Longevity: Maintenance and Inspection
Like any structure, a concrete pool requires regular maintenance to ensure its longevity. This includes regular cleaning, water chemistry testing, and inspection for cracks or leaks. Prompt repairs are essential to prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. Regular inspections by qualified pool professionals can identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventative maintenance. Proper winterization is also critical in colder climates, preventing damage from freezing temperatures.
The Human Element: Craftsmanship and Expertise
While engineering principles and advanced technologies play a vital role in concrete pool construction, the human element remains paramount. Skilled craftsmen, with years of experience and a keen eye for detail, are essential for bringing the design to life. From formwork and rebar placement to concrete finishing and waterproofing, meticulous craftsmanship is evident in every stage of the process. The expertise of pool builders and engineers ensures that the pool is not only structurally sound but also aesthetically pleasing and functional.
People Also Ask (FAQs):
-
What are the key factors to consider in concrete pool structural design?
- Soil analysis, hydrostatic pressure, reinforcement, concrete mix design, waterproofing, and expansion joints are crucial factors.
-
How do you prevent concrete pool cracks?
- Proper soil preparation, adequate reinforcement, expansion joints, and high-quality concrete mix design are essential.
-
What is shotcrete, and why is it used in pool construction?
- Shotcrete is pneumatically applied concrete that conforms to complex shapes and creates a monolithic structure. It’s ideal for pool construction.
-
How important is waterproofing for a concrete pool?
- Waterproofing is crucial to prevent water seepage, protect reinforcement from corrosion, and extend the pool’s lifespan.
-
What are the benefits of a concrete pool over other types of pools?
- Concrete pools offer design flexibility, durability, and customization, allowing for unique shapes and finishes.
-
How often should a concrete pool be inspected?
- Regular inspections, ideally annually, are recommended to identify potential issues and ensure longevity.
-
What type of reinforcement is used in concrete pools?
- Steel rebar is the most common reinforcement, arranged in a grid to provide tensile strength.
-
What is hydrostatic pressure and how does it effect a pool?
- Hydrostatic pressure is the force exerted by water. It increases with depth and needs to be accounted for in the structural design to prevent pool wall failure.
-
How long does a concrete pool last?
- With proper construction and maintenance, a concrete pool can last for many decades.
-
What are expansion joints in a pool?
- Expansion joints are flexible materials placed in the concrete to allow for movement from temperature changes and minor ground shifts, which prevent cracking.
Conclusion: A Testament to Engineering and Artistry
Concrete pool structural design is a testament to the harmonious blend of engineering principles and artistic craftsmanship. It’s a meticulous process that demands expertise, precision, and a deep understanding of materials and forces. From the initial soil analysis to the final interior finish, every stage contributes to the pool’s overall integrity and aesthetic appeal. A well-designed and constructed concrete pool is a lasting investment, providing years of enjoyment and enhancing the value of any property. By understanding the intricate details of concrete pool structural design, homeowners can ensure a safe, durable, and visually stunning aquatic retreat. The pool, in its finished state, is not just a body of water, but a testament to human ingenuity, and a space where memories are created.
Read More: The Hidden Dangers Lurking in Your Unclean Pool: A Comprehensive Guide




